- Coinsurance Deductible Copay
- Is It Better To Have A Copay Or Deductible
- Copay Plan Vs High Deductible
- Insurance Copay Vs Deductible
In title insurance, it also means the sharing of risks between two or more title insurance companies. In health insurance. In health insurance, copayment is fixed while co-insurance is the percentage that the insured pays after the insurance policy's deductible is exceeded, up to the policy's stop loss. You'll pay either our full copay rate or reduced copay rate. If you live in a high-cost area, you may qualify for a reduced inpatient copay rate no matter what priority group you're in. To find out if you qualify for a reduced inpatient copay rate, call us toll-free at 877-222-8387. We're here Monday through Friday, 8:00 a.m.
In insurance, co-insurance or coinsurance is the splitting or spreading of risk among multiple parties.
In the United States[edit]
In the U.S. insurance market, co-insurance is the joint assumption of risk between the insurer and the insured. In title insurance, it also means the sharing of risks between two or more title insurance companies.
In health insurance[edit]
In health insurance, copayment is fixed while co-insurance is the percentage that the insured pays after the insurance policy's deductible is exceeded, up to the policy's stop loss.[1] It can be expressed as a pair of percentages with the insurer's portion stated first,[2] or just a single percentage showing what the insured pays.[3] Once the insured's out-of-pocket expenses equal the stop loss the insurer will assume responsibility for 100% of any additional costs. 70–30, 80–20, and 90–10 insurer-insured co-insurance schemes are common, with stop loss limits of $1,000 to $3,000 after which the insurer covers all expenses.[4]
In property insurance[edit]
Co-insurance is a penalty imposed on the insured by the insurance carrier for underinsuring the value of the tangible property. The penalty is based on a percentage stated within the policy and the amount underreported.[5]
In title insurance[edit]
Owner's title insurance policy forms of the American Land Title Association created between 1987 and late 2006, contain co-insurance clauses. For partial losses, they require the insured carry a percentage of the risk of loss in two circumstances. The first is if the insured did not insure its title for at least 80% of its market value at the time the policy was issued. In that case, the insurer will pay only 80% of the loss. The second is if improvements constructed on the property after the policy is issued increase the property's value by at least 20% above the amount of the policy. In that case, the insurer will pay a percentage of the claim equal to the ratio of 120% of the amount of insurance purchased divided by the sum of the amount of insurance and the cost of the improvements.[6]
Co-insurance is also used among U.S. domestic title insurers in a manner similar to that described below for the international insurance market.
In other insurance[edit]
Coinsurance Deductible Copay
In some cases, including employer's liability insurance, co-insurance percent denotes a function analogous to the copay function that it has in health insurance, in which the insured covers a certain percentage of the losses up to a certain level.[7]
In business income interruption insurance, a type of time-element insurance,[8] the co-insurance percent indicates how long the coverage will last, and can range from 50% to 125%. The former co-insurance allows for 6 months of coverage, compared to 15 months for 125%.[9]
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^'2006 Medical Plan Frequently Asked Questions'. UPS.edu. University of Puget Sound. What is the difference between co-payments, coinsurance, and deductibles? (entry). Retrieved 2020-01-29.CS1 maint: discouraged parameter (link)
- ^'Health Plan Explained'.
- ^glossary. coinsurance
- ^What Is Coinsurance?Archived 2009-02-27 at the Wayback Machine. Insurancelane.
- ^'What Are Coinsurance Clauses and Do Courts Enforce Them? | Property Insurance Coverage Law Blog | Merlin Law Group'. Property Insurance Coverage Law Blog. 2011-09-29. Retrieved 2020-08-31.
- ^See, for example, Conditions and Stipulations No. 7(b) of the 1992 ALTA Owner's Policy.
- ^StudentCover. What is Coinsurance? Know more about Copayment/Copay.
- ^Miller M, Garko M. (2008). Time Element Coverage.
- ^Taking time out for time-element insurance. American Agent & Broker.
External links[edit]
- Insurance to Value from the Casualty Actuarial Society
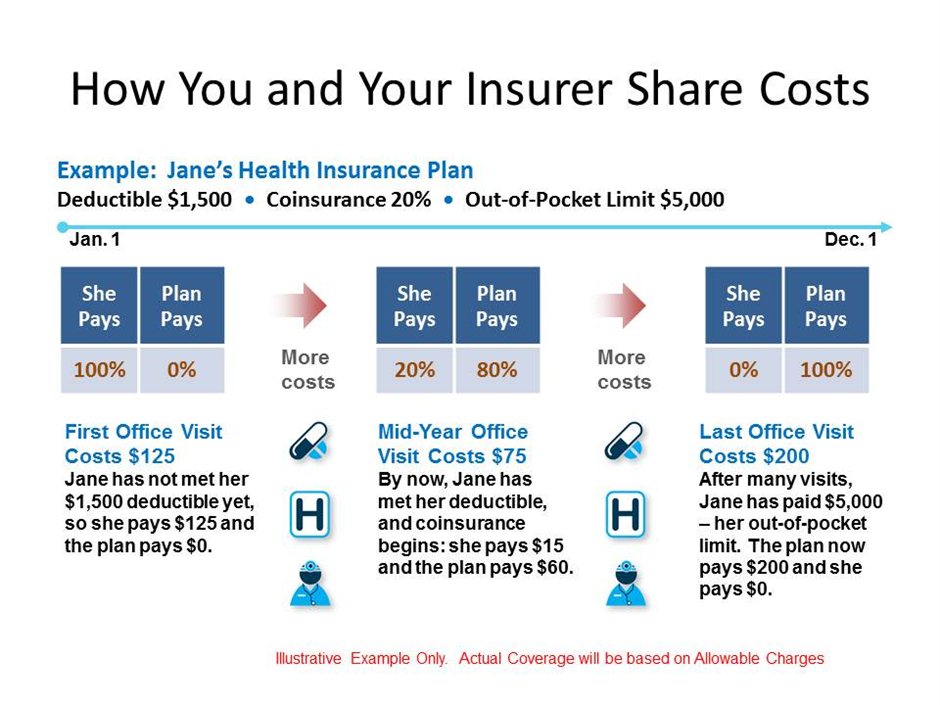
It is important to understand how your health care plan operates, but far too often the tricky benefit jargon of “deductible, coinsurance, copay, and out-of-pocket max” get in the way. These hard to understand health care vocabulary terms are explained below to help make understanding your health care plan much simpler!
Deductible – the amount of out-of-pocket expenses you pay for covered health care services before the insurance plan begins to pay.

| HSA-Eligible Plan | All covered services require you to meet your deductible first and then services will be covered through coinsurance. |
| PPO Plan | Some covered services require you to meet the deductible first, while other covered services are paid with a copay. |
| Helpful Hint! | The health plan comparison chart shows deductible amounts for Tier 1, Tier 2 and Tier 3, but you should think of your deductible as one sum of the money you have paid for your services. |
| Example | With a $1500 Tier 1 deductible on the HSA-Eligible Plan with single coverage, you pay the first $1500 of covered services yourself. If you have met this, you would pay an additional $100 towards your services and then would have met the Tier 2 deductible of $2,500. |
Coinsurance – the percentage of cost of a covered health care service you pay once you have met your deductible.
| HSA-Eligible and PPO Plans | For services covered by “coinsurance after deductible” the amount you pay in co-insurance continues to count towards meeting your next Tier deductible. |
| Coinsurance % | Most Tier 1 services are covered at “90% coinsurance after deductible,” while Tier 2 services are “75% after deductible and Tier 3 are “60% after deductible.” |
| Example | If you are on either plan and have hit your Tier 1 deductible and visit a Tier 1 urgent care provider, the plan covers that service at “90% coinsurance after deductible.” This means you will pay 10% of the cost of the visit and your insurance will cover the remaining 90%. The 10% you pay will count towards your deductible. |
Copay – a fixed dollar amount you must pay to a provider at the time services are received.
| PPO Plan | Only the PPO Plan offers a copay option for specific covered services. Your copay does not count towards your deductible. |
| Copay Amounts | Copay amounts vary based on the plan design. The health plan comparison chart is the best resource to understand what your copay is for a covered service within any of the tiers. |
| Example | If you are on the PPO plan and you see a Tier 1 provider for a standard sick visit, then your copay at the time of the visit will be $20. If you seek a Tier 1 provider for physical therapy, then your copay will be $35. |
Is It Better To Have A Copay Or Deductible
Out-of-Pocket Max – the maximum amount you pay each calendar year to receive covered services after you meet your deductible. Once you meet your out-of-pocket maximum, the Plan pays 100% of covered services you receive. In network and out-of-network services are subject to separate out-of-pocket maximums.
Copay Plan Vs High Deductible
Insurance Copay Vs Deductible
| HSA-Eligible and PPO Plans | Your out-of-pocket max is the summation of everything you have paid for your medical services received; this includes deductible, coinsurance and copay. |
| Helpful Hint! | Out-of-pocket max’s are determined by coverage level (single vs plan with dependents) and salary. On the health plan comparison chart you will see multiple rows with Out-of-Pocket Max figures, so be sure to look in the row that pertains to your situation. |

